When we talk about abs, or abdominal muscles, the first thing that comes to mind is the flexing of a fatless six-pack. But apart from showing off, their main function is to maintain a stable core and facilitate different movements of the trunk. Whether on the sports field or yoga mat, your six-pack abs are always a great bonus, enhancing skills in more fields than you can imagine. No matter whether you are a sprinter who covers the distance in a few seconds or a yoga practitioner who stretches for as long as the pose, the function of your abdominal muscles in providing stability and strength is indispensable not only for optimal performance but also for injury prevention. Prepare yourself for a unique trip down into the inner-self of human anatomy, and this time we will focus on the well-guarded secrets of the abdominal muscles.
Origin and Insertion Points
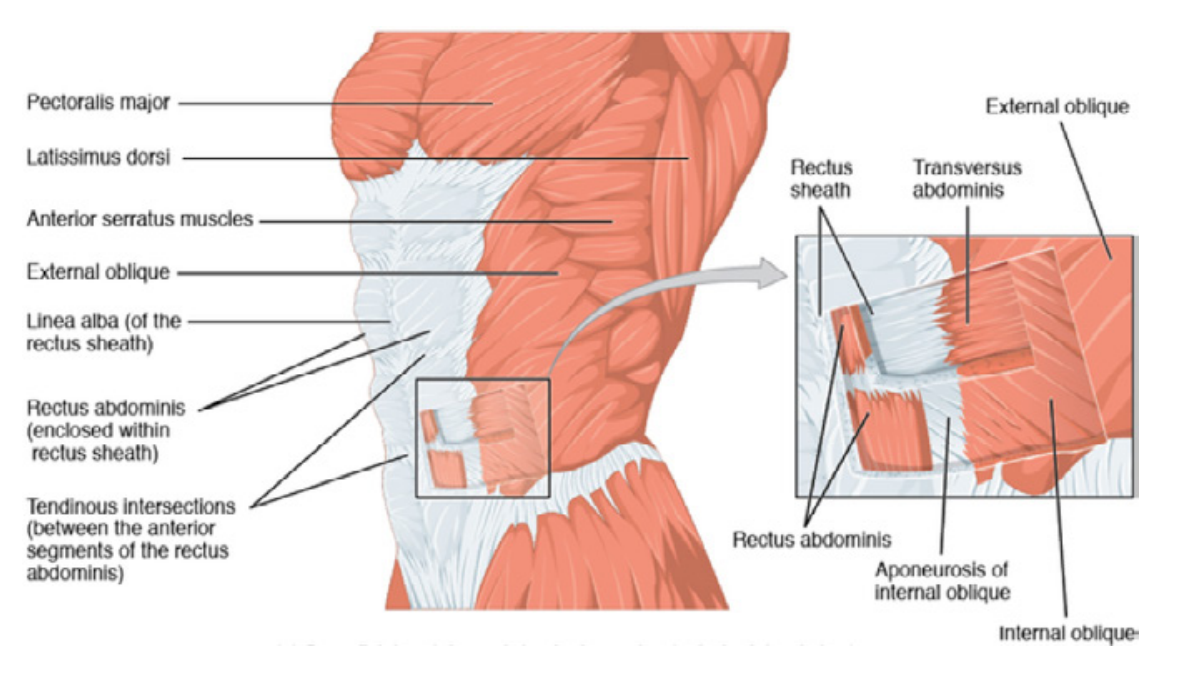
Nestled in the anterior torso, the abs muscles consist of four main groups: the rectus abdominis, external obliques, internal obliques, and transverse abdominis.
Rectus Abdominis
Generally referred to as a “six-pack,” the rectus abdominis is the paired muscle that makes the anterior abdominal wall. That’s why it is the one functioning the normally to bend the lumbar spine and to compress the abdominal contents.
External Obliques
The external obliques muscle is located along the lateral and anterior part of the abdomen. They bear the load of the trunk while performing rotational and lateral movements, thus guaranteeing balance and steadiness.
Internal Obliques
This muscle is situated underneath the external obliques and helps in engaging trunk rotation, lateral flexion, and frontal flexion. Together with the external obliques, this muscle maintains stability within the core.
Transversus Abdominis
The innermost layer of the abdominal muscles, the transversus abdominis, performs the vital functions of core stability and acts like a natural corset, which helps in supporting the spine and the pelvic region.
Functions of Abs
Core Stability
The role of abs in stabilization of our body cannot be overstated. They are essential in ensuring balance while performing movements, they greatly reduce the chances of getting injured and they enhance agility during physical activities.
Spinal Support
Having a strong core enhances body stability and makes it possible to generate force with better ergonomics, thereby avoiding back pain.
Breathing
Abdominal muscles are involved in breathing process, provide a helping push for the forced exhalation by squeezing the abdominal stuff and the air being cleared from the lungs.
Posture
The core muscles are the base of our posture; they eliminate imbalances, as well as problems such as kyphosis and lordosis.
Movement
At the core, the abs muscles allow movement related to bending, twisting, and lifting to be facilitated through the provision of stability and transmission of power to the core and upper body.
Abdominal muscles are more than an aesthetic benefit, they are essential to maintaining core stability, supporting the health of the spine, and facilitating movement. Through study of anatomy, functions and origin of abs, people may understand the ways in which they can incorporate these in their strength training or build good health and fitness.





Leave a Reply